How does DHCP work in the network? Before we answer that question, we need to understand the different ways of configuring the IP addresses.
You could use either DHCP or static IP configuration.
You might already know the configuration of IP address statically on a computer.
It requires you to go to the network properties of the network hosts and manually assign the following.
First, you configure the IP address, the subnet mask, and default router/gateway and DNS and so on.
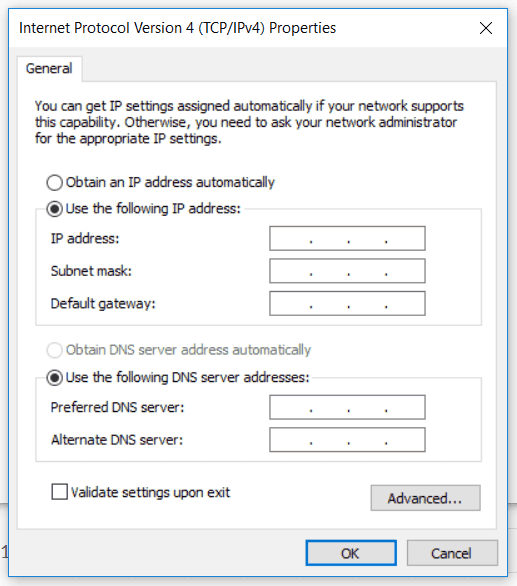
Imagine how much time does it take for you to configure the IP address for a single host? Maybe let’s say around a minute or two, right?
Now, given that scenario Let’s suppose you have Hundreds or even thousands of network hosts on a network that requires IP addresses.
Is it possible for you to assign IP addresses on the network hosts manually on each device one by one?
Yes, It’s possible but takes HOURS and HOURS to configure them as it’s a static IP configuration.
However, there should be a better way to automate this process, and Yes, there is a better way. That’s when DHCP ( Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) comes to your rescue.
What is DHCP and how does it work?
The DHCP ( Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) fixes the above problem by configuring or assigning an IP address on the network devices automatically. Not only just IP address other parameters too, with the help of DHCP options.
A client can request an IP address, and the DHCP Server would serve the request by using DHCP DORA process.
In this blog, we are going to find out how does DHCP works in a network and take a look at some of the essential DHCP packets using Wireshark.
What is the DHCP DORA process in detail?
The best way to remember how does DHCP process works is by remembering the Acronym DORA, which translates to,
D – Discover
O – Offer
R – Request
A – Acknowledge
It looks like below.
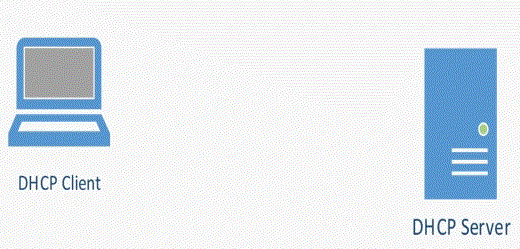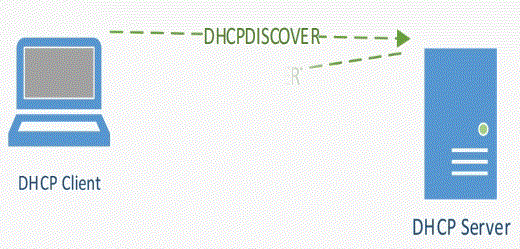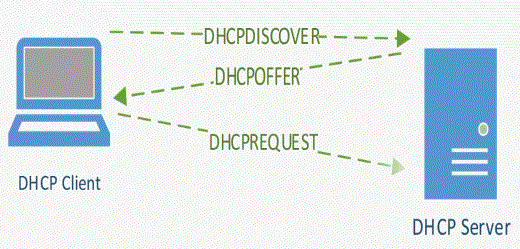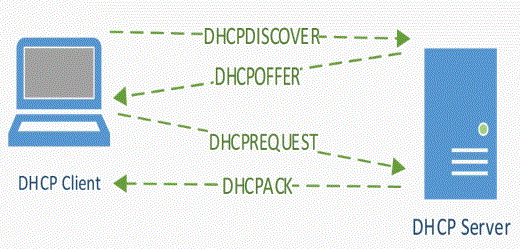
I ran some packet capture on my network and now lets look at each DHCP packet using the Wireshark capture.
- What is DHCP discovery?
- What is DHCP offer?
- What is DHCP REQUEST ?
- DHCPACK packet
What is DHCP excluded address?
1. What is DHCP discovery?
The moment a DHCP enabled client connects to the network whether it’s wired or wireless,
Step1. It sends the DHCP Discover message on the network as a broadcast, In this example, let’s suppose the DHCP client is ‘Client A’ and it sends the DHCPDISCOVER message out to the network.
Step 2. L2 switch who receives this message, forwards this broadcast to all its connected interfaces, except the interface where the broadcast message received from, which is ‘Client A’ interface.
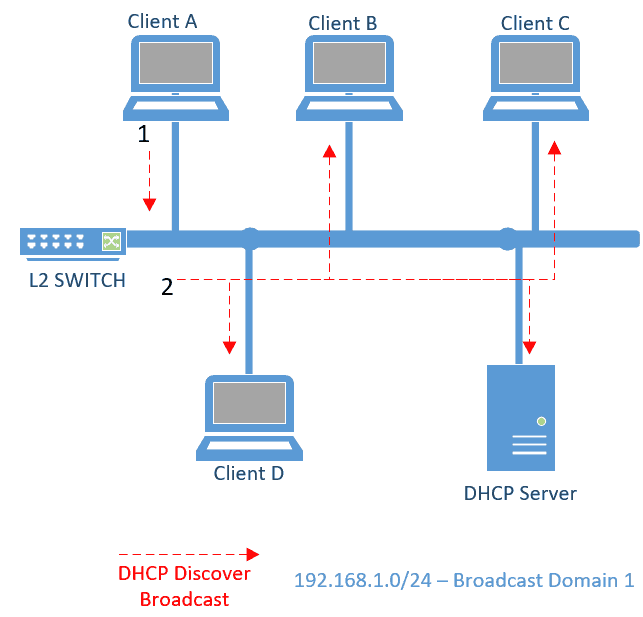
When this DHCPDISCOVER broadcast received by all the hosts in the network, all of them would ignore the broadcast packet, except the DHCP Server. Let’s look at this DHCPDISCOVER packet in more detail with Wireshark packet capture.
a. DHCPDISCOVER packet in Wireshark.
This DHCPDISCOVER would show Layer 2 source mac address as the DHCP client ‘Client A’ mac address, and DHCP destination mac address would be ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff which is a broadcast mac address

b. DHCP discover packet format.
Since its broadcast, the source IP of the DHCPDISCOVER packet would be 0.0.0.0, of course, DHCP client doesn’t have an IP address to begin with, which we would get it eventually:).
Also, destination IP would be 255.255.255.255, see below.

You can also see that DHCP uses UDP port 68 for the client and 67 for Server communication.
When I expand the final datagram field, I could see more details about this protocol. Such as, This is a DHCP Discover packet, and I could see the client IP, client MAC address, DHCP Options, which are different in each client and Server DHCP communication.
You can also see the same DHCP Hostname in DHCP Discover options again, and this should be the DHCP client hostname.

2. What is DHCP offer?
The DHCP Server which is listening to these DHCP Discover packets on the UDP port number 67, would receive this DHCPDISCOVER packet.
Now the DHCP Server has to serve this request by look into its DHCP scope which configured earlier and picks an IP from the subnet and assigns it to the DHCP client.
In our scenario, we have DHCP scope of 192.168.1.0/24, in which I am excluding the first 20 usable IP’s (192.168.1.0-192.168.1.20) using DHCP excluded-address
Note: If you are interested in configuring DHCP on cisco devices step by step, you may click here.
The Server would pick an IP from the address pool and responds with the message DHCPOFFER as BROADCAST again.
It’s kind of like a person going to a hotel and trying to book a room, and the receptionist showing the room number and says this is the room number you could stay for the next 24hours, are you okay with that:). Similarly, the DHCP Server would ask the client in the offer message. I am assigning this IP address to you. If you are okay with it, you can request it.
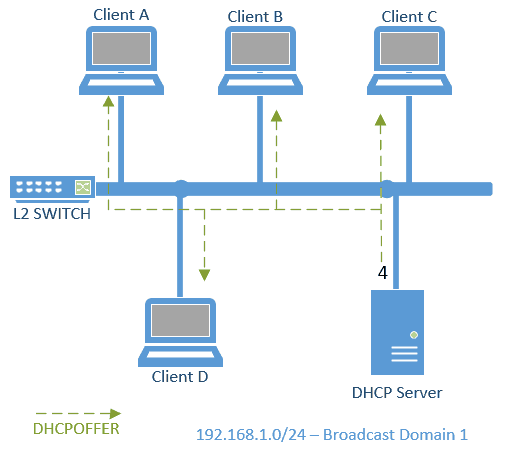
a. DHCP OFFER packet in Wireshark.
You can see an ethernet source address as DHCP Server Mac address, and destination is a broadcast address ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, it’s opposite to what we saw in the DHCPDiscover packet.
The second field is IP packet header, where you can locate the Server source IP as 192.168.1.5 and destination again broadcast IP address 255.255.255.255
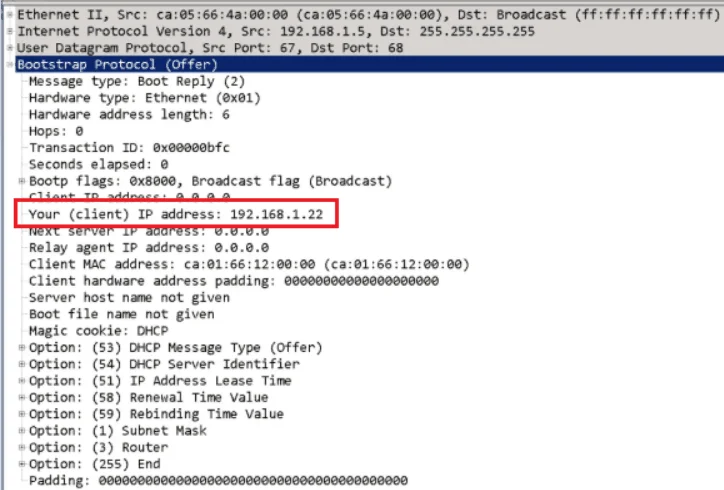
The final one in this Wireshark packet capture is Bootstrap Protocol (Offer) which translates to the DHCP offer, this is where you should see actual IP that the DHCP Server is going to assign to the client, see the highlighted part.
b. What are DHCP options?
DHCP options you can think of it like terms and conditions and additional facilities you would get when you rent/lease a hotel room.
Now a day’s modern network carries more DHCP options than what traditional network did, the traditional network used to use only a few of the options.
Let’s look at the important options under this DHCP offer packet now.

DHCP Option 53 would tell that it’s a DHCP offer packet.
That was an easy one, wasn’t it?
Option 54 known as DHCP Server Identifier, it tells the client that the DHCP Server IP address is 192.168.1.5
c. DHCP Lease time
The DHCP lease time is the amount of time that the client can keep the IP address in its configuration. When the lease time expires, the client should request for the new IP, but there is more to it. Let’s look at them now.
Option 51 – This is where the client gets to know the DHCP lease time. By default DHCP lease time is 24hours. You can change the default value as per your wish, the more you reduce the DHCP lease time, the more clients would send the DHCP packet, it’s not a good idea when you have more devices on the network to reduce the DHCP lease time.
d. DHCP renewal time
Now you might be thinking what this Option 58 renewal time Value is?
This value is half of the DHCP lease time, in our case 12 hours since we are following the default lease time, which is 24hours.
Upon reaching the DHCP renewal time the client would send DHCPREQUEST as unicast to the Server as they both already know how to get to each other by now, and the Server responds as DHCPACK, now the client can keep the leased IP and reset the DHCP lease time to its default, again 24hours.
e. DHCP Rebinding Value
What if the Server doesn’t respond to the DHCP request?
At that time, the client would keep sending the DCHPREQUEST until it reaches DHCP rebinding value which is option 59.
After the rebinding time which is 21hours in our case, the DHCP request which the client was sending as unicast would change to broadcast to see are there any other DHCP Server on the network who can serve this DHCP request.
Options 1 and 3 are straightforward. They represent the subnet mask of the IP address and Default gateway/Router respectively for the client.
Now you got a bit of idea about the DHCP options. There are a whole lot of options available under DHCP since I can’t explain all of them in this blog, you can check out all the DHCP options here.
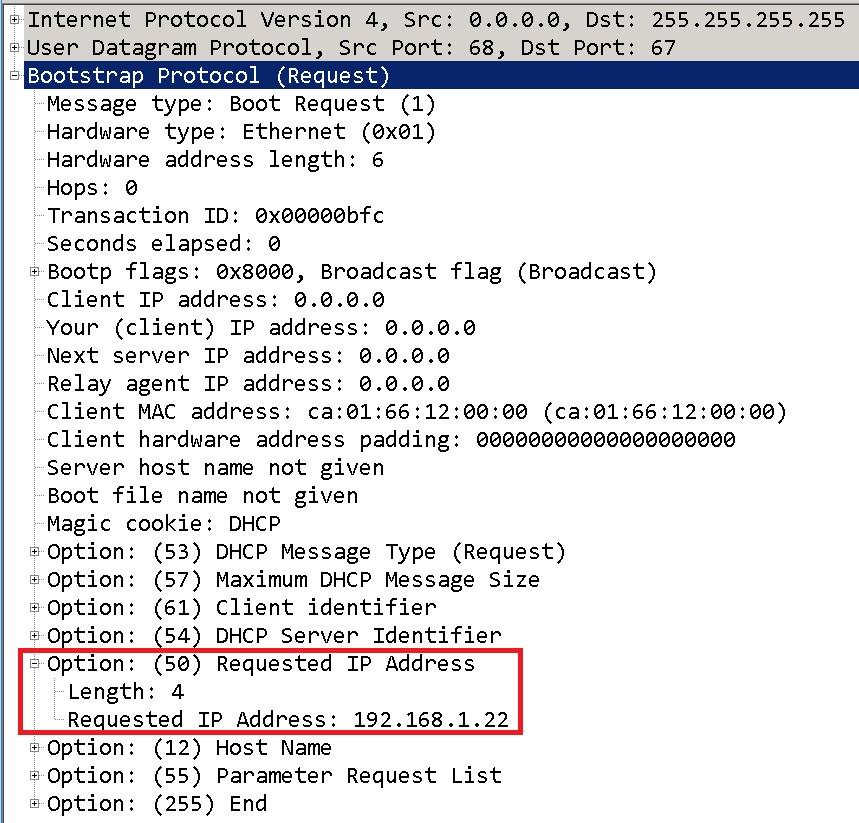
3. What is DHCP REQUEST ?
Its time for the client to respond to the DHCPOFFER it received from the DHCP Server with DHCPREQUEST, this DHCP request message says I am okay with the IP you offered and let me request for the same.
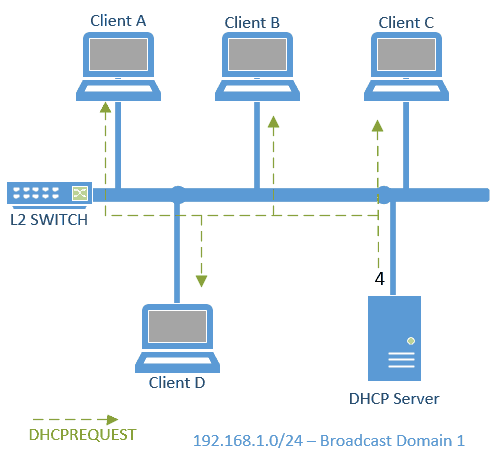
you can see option 50 in DHCPREQUEST which says the requested IP is 192.168.1.22
DHCP request is broadcast or unicast?
We still haven’t assigned the IP address to the network host, so the DHCP request is still a broadcast message.
a. DHCP REQUEST in wireshark.
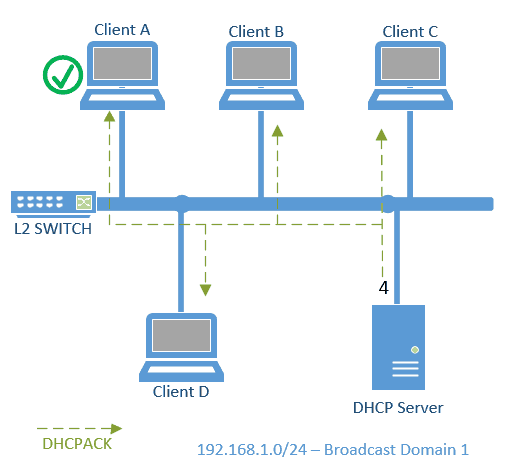
4. DHCPACK (DHCP Acknowledgement)packet
The final step of the dhcp process is known as DHCPACK.
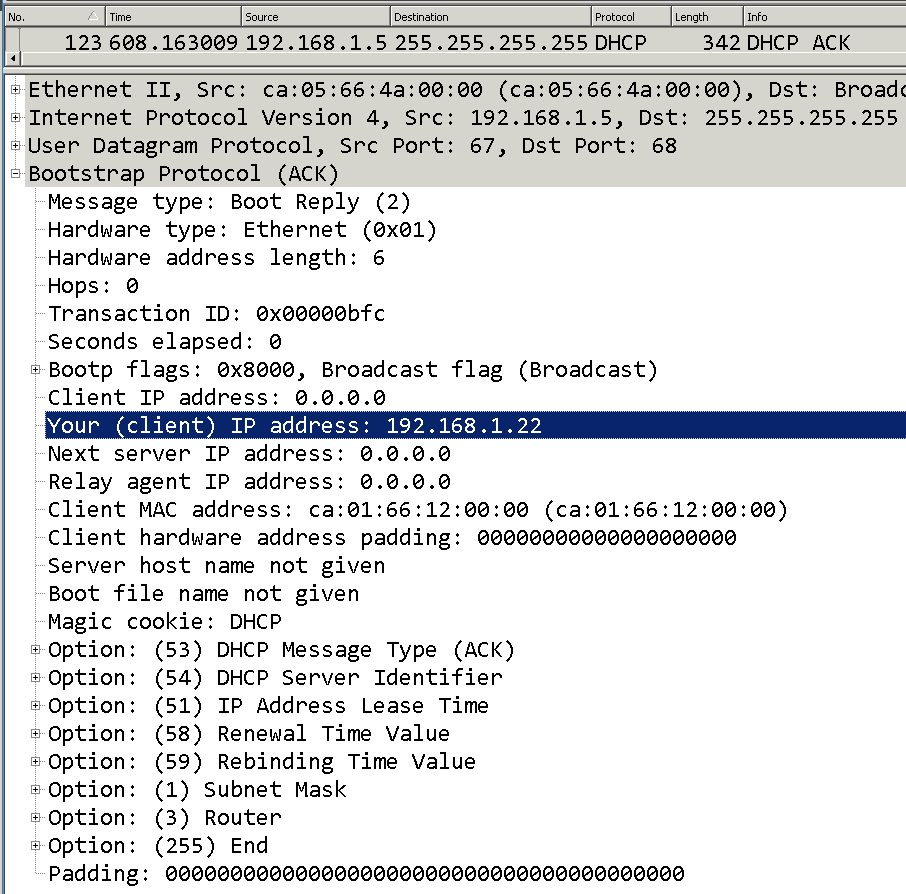
In this step, the DHCP Server has to acknowledge that it has leased the IP to the client-A and it can use that IP 192.168.1.22 for the next 24hours.
Let’s look at the DHCPACK packet in wireshark and as you can see the client IP in the packet capture.
What is DHCP excluded address?
Remember I talked about DHCP excluded-address. What is it?
In some IP networks, network hosts don’t require IP to be configured by the DHCP, such as Printers, Servers, Network equipment, etc. Since its IP would never change and mostly it would also have a DNS entry associated with it.
The network administrator prefers to be configured these IP addresses statically.
How do I exclude addresses in DHCP?
While configuring the DHCP address pool and its scope, you can assign any of the ranges from the subnet to allocate for the DHCP excluded-address.
E.g., in the subnet 192.168.1.0/24, we can have 254 IP addresses starting from 192.168.1.1 to 192,168.1.254.
We can exclude the subnet range starting from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.20.
When I add this exclusion, the DHCP Server starts to assign the IP starting from 192.168.1.21.
I hope now you know how the DHCP works and a bit of understanding of what are the important DHCP options.
In case if I have missed something you can let me know in the comment section below.
Lavisha
Tuesday 26th of December 2023
Excellent Article. It helped me a lot to understand about DHCP. Thank you!