I have covered many blogs on how you can install a network device in gns3. However, sometimes the challenge is to get the gns3 devices to talk to the local network or your host PC.
If you get that setup, you can access the network device GUI from your local machine browser or ssh from it.
Let’s look at how you can connect local PCs to the gns3 inside devices, such as routers and firewalls, or any network devices for that matter.
Requirements.
- A VMware workstation pro. You don’t need to have a license as we won’t be using it to spin up any VM’s in it. We are just using it to get the virtual adapter created within GNS3.
The one which I have is a licensed version, though.
- Gns3 installed on a windows machine.
Read also,
How to Install Palo Alto in GNS3?
Gns3 Common Errors And How To Fix Them.?
How to Integrate VMware, VirtualBox, Qemu Vm’s in GNS3 ?
How I have setup my GNS3 | 10 Easy steps.
How To Install Checkpoint Firewall In Gns3?
How To Install Pfsense Firewall On GNS3?
Easy way to connect GNS3 to the internet on Windows host.
Setup the virtual adapters.
What is a virtual network adapter?
If you are not familiar with virtualization and wondering what a virtual adapter is, it is very simple.
The virtual adapter is similar to the physical adapter but created with the help of software. It is not physically present in the system. It is a virtual device.
Moreover, identical to how you interconnect different hosts in a network using a physical local area network, you can also do so with virtual adapters. Most of the VM’s on the cloud uses the virtual network adapters.
In the GNS3, it also uses Linux bridging technology to create different network segments using virtual adapters.
When you look at a GNS3 topology, and you see all the network hosts connected to each other right? All those network connectivy is made up of virtual network adapter.
Now we need to extend those virtual network out from the GNS3 to your local machine, and your local machine will also become part of the GNS3 topolgy.
To achive that, we need to install VMware workstation pro, this is the easiest method which I tested.
After you have installed the VMware workstation pro, you may open it and close it. That way, it should get its services automatically started as well.
For the GNS3 to connect to the local PC, you need to create two virtual adapters.
One, I can use it for the router SSH, and another for the firewall web GUI.
Now you may open Gns3 and click on edit preferences.
In the Preferences window, click on Vmware and then click on Advanced local settings.
You should be able to see something called Managed Vmnet interfaces.
I will be configuring VMnet 5 for the router access and Vmnet 6 for the firewall access.
So I selected the virtual adapters from Vmnet5 – VMnet6 and then clicked on configure.
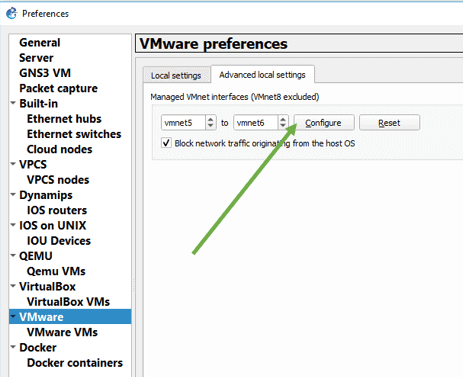
It should now configure both the virtual adapter on your PC.
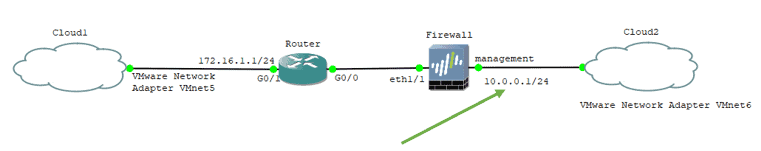
Let’s look at our topology now. I have a router with an IP address of 172.16.1.1/24, and the firewall has a 10.0.0.1/24 network. For the lab purpose, let’s assume both the above network that I will use as the management subnet.
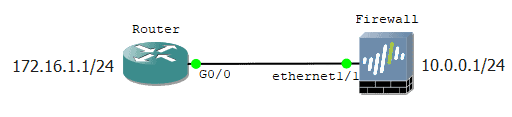
Connect the GNS3 Router to the localhost.
Let’s talk about Router, I have one interface configured with 172.16.1.1, so I should also make either vmnet5 or 6 to be part of the same network. That way, the virtual adapters can talk to the device within the same network.
I am going to choose VMnet5 for router management.
In your windows machine, goto start Run and type ncpa.cpl in the prompt and click on OK.
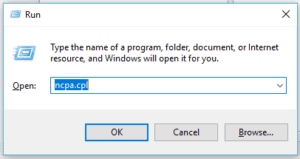
Right-click on VMnet5 and click on Properties.
In the VMnet5 properties, double click on Internet protocol version 4.
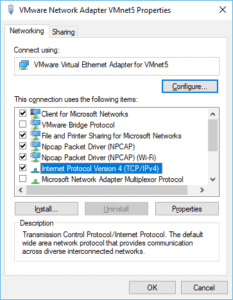
And configure an IP from the same subnet, I will configure 172.16.1.10/24 then click on OK.
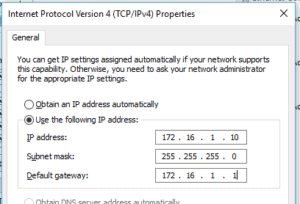
Connect the virtual adapter to the Router.
Alright, you configured the virtual adapter on your PC. Now that adapter needs to connect to the Router to communicate, how do I achieve that?
For that, click on Browse end devices, and drag and drop the cloud to the topology.
When it prompts you to choose the host to connect to, choose your local machine to set up the virtual adapter.
Right-click on the cloud and click on Configure.
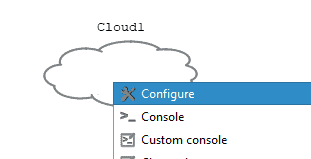
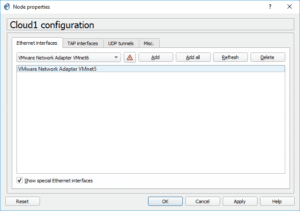
In the cloud-1 configuration window, check the option that says ‘Show special ethernet interfaces’ and remove all the physical interfaces you see by the local machine.
Now from the dropdown, select VMnet5 and click on Add. And then click on, OK.
Connect the cloud now to the router interface, where you have the 172.16.1.1 network configured.
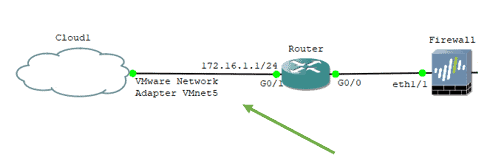
That’s it. Let me check the router configuration.
I can see the interface that I just connected came up now, and the same interface associated with the IP from the same subnet.
Router# *Oct 13 05:52:50.581: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up *Oct 13 05:52:51.581: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up Router# Router# Router#sh ip int brief | ex un Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol GigabitEthernet0/1 172.16.1.1 YES manual up up Router#
let’s try to ping the local machine from the Router.
Router#ping 172.16.1.10 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.1.10, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 3/68/116 ms Router#
Cool, that worked fine. Let me also do a ping from my local machine as well, just to make sure all looking good.
As you can see, I can ping the same device from within the local machine itself.
You should now be able to ssh the Router from your local machine and jump to other hosts if you have so many hosts in the topology.
Connect GNS3 firewall host to the local network.
Just like how you configured the GNS3 Router to the physical network, let’s go ahead and configure a second virtual adapter, which can use to access the web GUI of the firewall.
Go to start run and type ncpa.cpl
Right-click on the VMnet6 and configure the IP address 10.0.0.15/24
Add a cloud to the network. Now you may right-click and click on configure.
Like you did right-click on the cloud and configured the cloud for Router, we will do the same thing for the second cloud.
From the interface dropdown list, select interface VMnet6 and click on Add. Then click on OK.
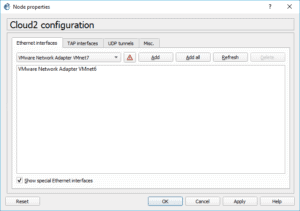
You may add the cloud to the topology. And connect to the firewall interface.
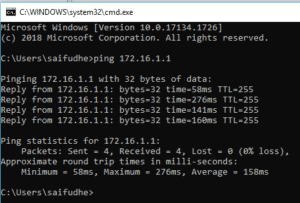
As you can see, I can ping the firewall IP 10.0.0.1 now. Let me also try to access the firewall web GUI from my local browser and see if I can access it or not.

As you can see, I can access the firewall GUI.
And this is how you can connect your local machine to the device inside the GNS3. Though I showed how you could access the devices using two clouds devices, you don’t really need to configure multiple clouds for the purpose.
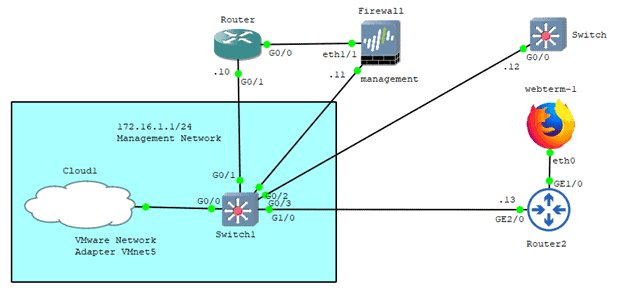
If you have multiple devices with the same management IP subnet, you can connect all the devices to a switch and switch to the cloud.
For example, see below, I have network devices such as firewalls, routers, and switches configured to be on the same Management subnet 172.16.1.0/24, and each of those devices has IP’s from the same subnet as well. Which again connected to a switch and the switch also connected to the cloud that we configured earlier on the same subnet.
Troubleshooting tip: Like any other opensource software, this method isn’t perfect, there will be times when you keep your laptop to sleep, and when you come back and start the lab again, you will be surprised to see the network which used to work no longer working.
And your local machine unable to talk to the gns3 devices. Or the cloud side, the interface wouldn’t come up.
I know it will be frustrating to troubleshoot those.
Whenever you get into those situations, this is what you have to do.
Goto edit preferences, and in the VMware, click on advanced settings and try to create VMware virtual adapter again.
But you have to keep one thing in your mind, though.
After you reset the adapter, it will start using its default IP addresses, which will be different from what you configured, so you will have to go back to the network adapters settings and change the IP address according to your network.